Don’t let your hair loss define you.
Affordable hair loss doctor-guided treatment options delivered directly to your door. Don’t let hair loss define you. Learn about your options.
GET STARTED

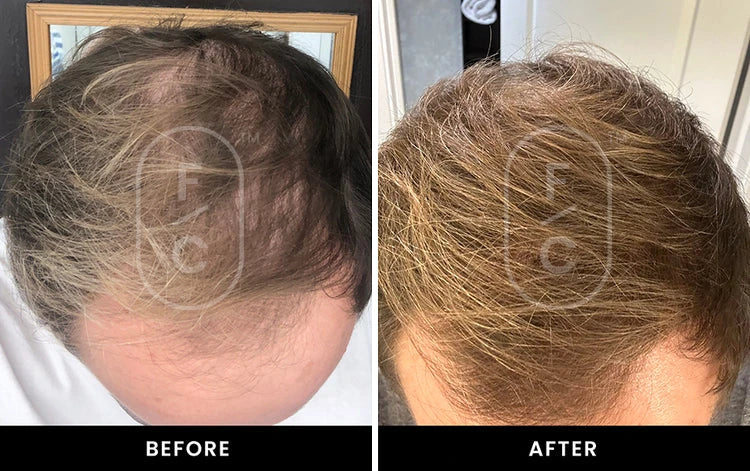
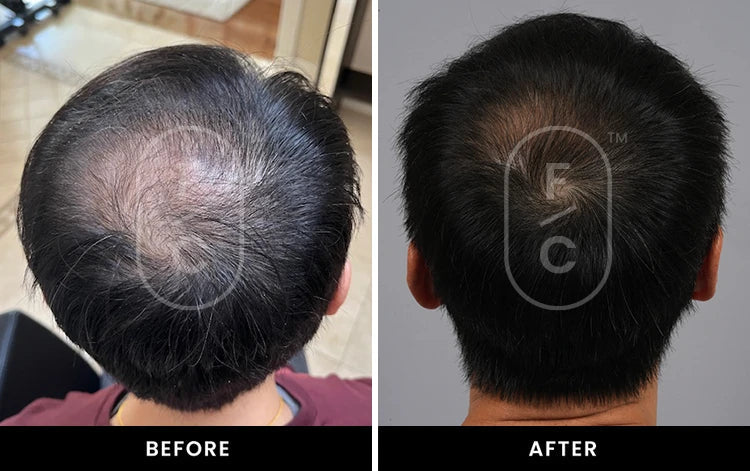
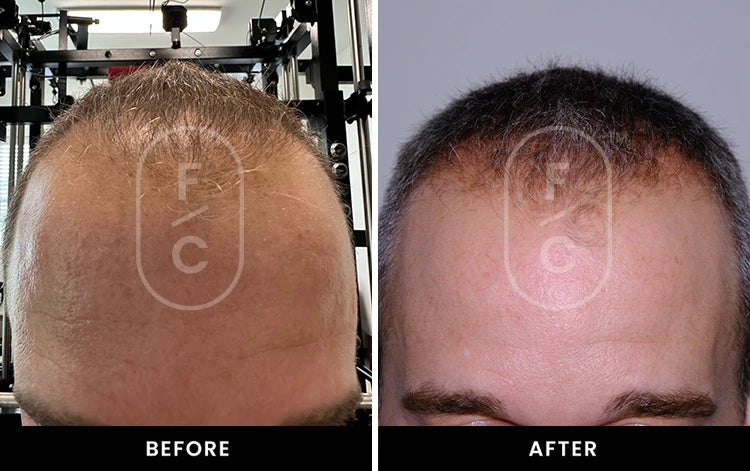
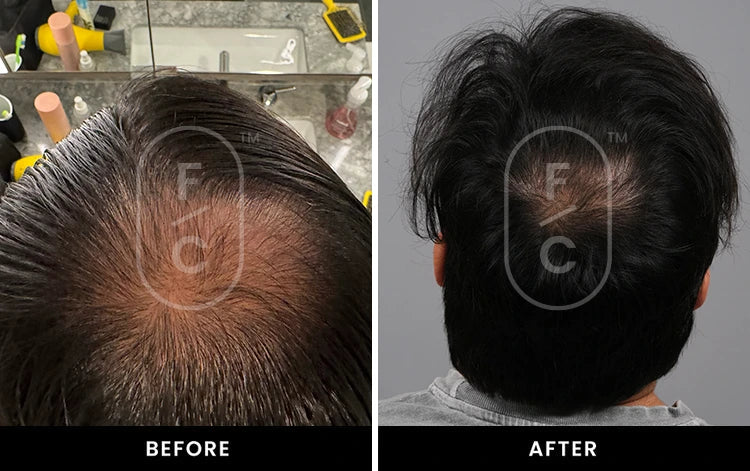
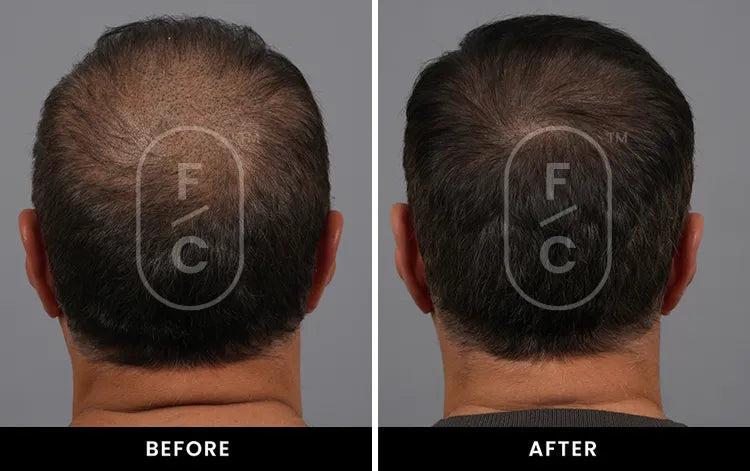
Real Results from Real Customers
Round out your confident haircare routine
Thickening Foam
Helps hair feel fuller and denser while delivering ingredients shown to help with growth.